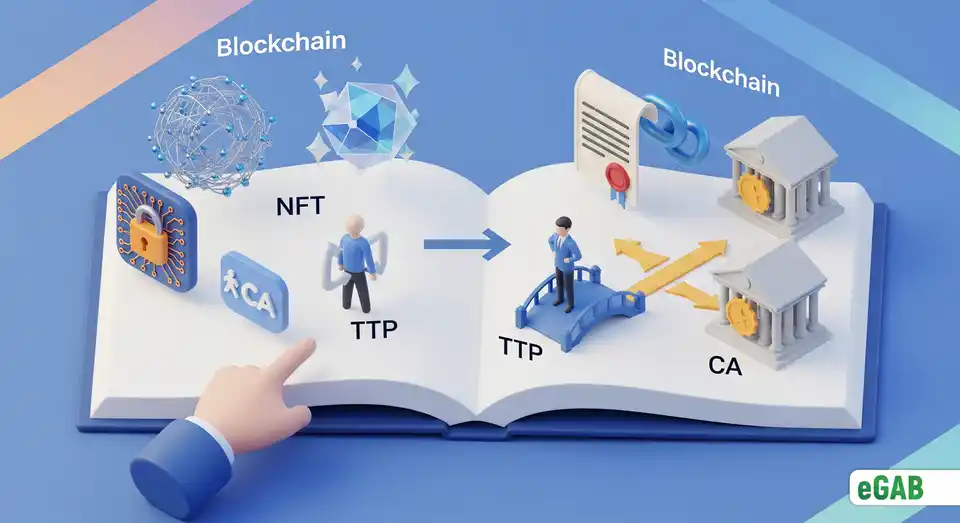
What Are Blockchain, NFTs, TTP and CA? The Simplest and Clearest Explanation
 Author:
Artem Grigoriev
Author:
Artem Grigoriev
- What is a database?
- What is a blockchain?
- What are centralised and decentralised blockchains, and which one is better?
- How does a database differ from a blockchain?
- What is an NFT (Non-Fungible Token)?
- What are digital documents?
- What is a TTP (Trusted Third Party)?
- What is a CA (Certification Authority)?
- What is a smart contract?
- What is a cryptocurrency?
- Want to dive deeper into the technical details?
- Summary: From Simple Folders to a Revolution in Digital Trust
Have you ever felt like the digital world is speaking a language you don't quite understand, casually throwing around terms like " blockchain ," " NFTs ," and " smart contracts "? It's easy to feel left behind when an exciting, powerful technology seems buried under layers of complex jargon. But what if the core ideas behind it all were actually simple? That’s the secret: they are. These aren't merely buzzwords; they are solutions to real-world problems of trust and ownership online. This article is your clear, simple guide, designed to break down exactly what blockchain , NFTs , a Trusted Third Party (TTP) , and a Certification Authority (CA) are, showing you precisely how they fit together to build a more secure digital future. You'll soon discover that genius is often found in simplicity. We're going to walk through each of these ideas using a simple analogy you already understand: paper documents and basic office supplies. Just follow along, and you'll see how it all clicks perfectly into place.
📘 This post is part of our comprehensive guide to "eGAB:The Global Academic Blockchain Ecosystem for Digital Credentials". Explore it to find answers to all your questions ;)
What is a database?
A database is simply a way of storing documents in an organized manner.
Think of a traditional database as a large ring binder, complete with many different dividers and clear pockets inside. You can neatly organize your documents into these pockets. What makes this binder so incredibly useful is its flexibility. At any time, you can easily pull a document out of a pocket, put a new one in, or just edit the one that’s already there . This inherent ability to easily change things is a core feature of databases, as they are specifically designed to efficiently manage information. For this, tech folks have a term: CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, and Delete). This fundamental difference is central to the blockchain vs database debate. This naturally leads to the question, how is a blockchain different from a database? Let's explore that next.

What is a blockchain?
A blockchain is also an organized way of storing documents. It's different, however, because all documents are securely linked to each other, much like the links in a chain.
So, what is blockchain technology, really? Now, let’s imagine a completely different kind of folder. This particular one has just a single, continuous pocket. When you want to add a new document, you don’t just slide it in. Instead, you have to securely glue it to the edge of the previous one . This process, which utilizes some clever cryptography (a method of protecting information through codes), creates an unbreakable, chronological (time-stamped) chain of documents. This chain of documents forms a digital ledger , and because it's protected by that cryptography, its immutability (the inability to be changed) is guaranteed.
Here's where it gets really interesting. What would happen if someone tried to mess with the chain, say, by ripping out one of the glued documents? The damage would be glaringly obvious. It's impossible to unglue a page without tearing the ones it's connected to. This blockchain explained simply, is a revolutionary method for ensuring data integrity (the accuracy and consistency of data), as it creates a perfect, unchangeable audit trail .

What are centralised and decentralised blockchains, and which one is better?
The debate over centralized vs decentralized blockchain architectures is all about control and accessibility.
In a decentralized blockchain , this special folder is not stored in one central location. Instead, you can think of it like a shared digital document where exact copies are held by thousands of independent people . These individuals are spread all over the world in a public peer-to-peer network (a network where participants share resources directly without a central server). It's a bit like a group project where everyone always has the latest version.
Here's where things get truly fascinating. If someone attempts to secretly alter a detail in their copy, the entire network instantly notices. Because that one copy no longer matches everyone else's, the system immediately flags and rejects it. This rejection process is governed by a consensus mechanism , a set of rules the network follows to agree on the state of the ledger. This is the core idea behind its exceptional security and transparency . Public blockchains are truly trust-free-not in the sense of being untrustworthy, but because you don't need to trust any single person or group in charge-which means no one can cheat the system.
Alternatively, let's talk about a centralized blockchain . In this case, these copies are shared only among a select group of trusted participants, typically within a single organization. In this setup, one entity retains control over who can add new documents to the folder. However, the "glued-together" structure of the chain is still in full effect. What this means is simple: even the controlling organization can't go back and secretly change a past record. Any attempt to do so would leave a very obvious, broken link in the chain. This process creates a fully verifiable and unchangeable audit trail (a step-by-step record of all changes), which is perfect for a private system.
So, which is better, a centralized or decentralized blockchain? Honestly, neither is fundamentally better or worse than the other. The right choice depends completely on the job at hand. For example, government systems that handle sensitive data, like your passport records, are usually centralized. Let's be real: you wouldn't want the general public to have a say in your official identity. That's a task best left to a secure, controlled environment.
An example of such an environment, within the world of digital educational documents, is eGAB (The Global Academic Blockchain Ecosystem for Digital Credentials).
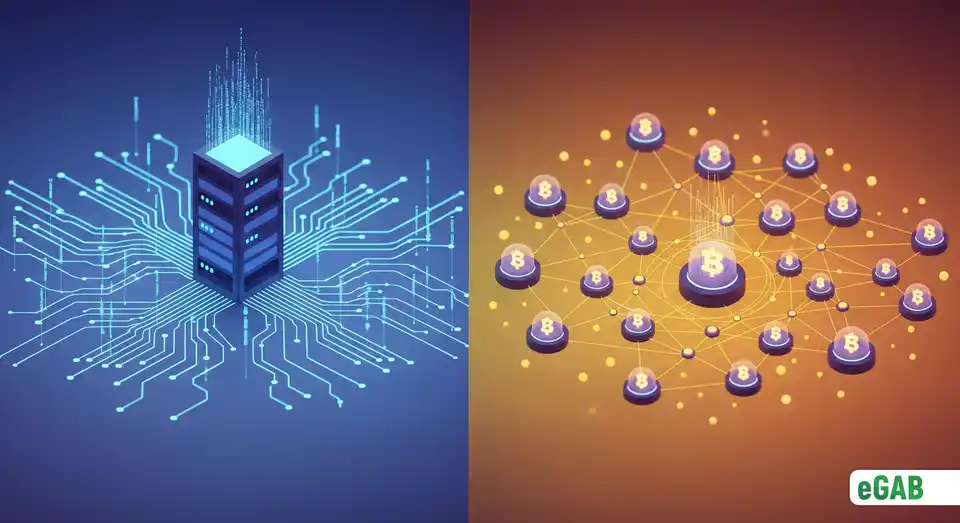
How does a database differ from a blockchain?
So, what is the bottom line in the blockchain vs database comparison? The main difference is this: in a regular database (our binder with pockets), you can easily and discreetly swap out any document. In a blockchain (the folder with glued-together pages), any change is instantly visible to the entire network, making secret edits practically impossible. Even authoritative bodies (official expert organizations) like the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) emphasize these key architectural (structural) differences.
To truly understand how is a blockchain different from a database , let’s break it down:
- Control: A regular database is centralized, which means a single owner calls all the shots. A blockchain, on the other hand, is decentralized and is managed collectively by all its participants.
- Immutability: Once you add something to a blockchain, it’s there for good; you can't change or delete it. You can only add a new record to show that a change has been made, which in turn preserves the full history. In a database, data can be altered or erased, often without leaving a single trace.
- Transparency: In a public blockchain, all records are typically visible to everyone on the network. This visibility creates a powerful layer of trust and accountability. Are you curious about the nitty-gritty details? The NIST's "Blockchain Technology Overview" report is a great technical resource.
What is an NFT (Non-Fungible Token)?
An NFT is simply one of the glued-together documents in our folder.
What is an NFT? It's a question that's been on many people's minds. Okay, so the blockchain is our super-secure folder with glued-together pages. But what in the world is an NFT? It's actually pretty simple. An NFT is each individual document that is held within the chain. Think of your NFT diploma or a special certificate as one of those glued-in pages; it has a specific, unchangeable place in the sequence. To understand how do NFTs work , you have to look at their unique place on the blockchain.
Thanks to its unique link to the "neighboring" documents in the chain, its authenticity is guaranteed. What makes it truly one-of-a-kind is its own data, which is called metadata (information that describes other information). This metadata includes details like your name, the date it was issued, and the course you completed. It also has information about its neighbors and its unique ID number. It is this verifiable uniqueness that makes it non-fungible , meaning it's impossible to replace with something else. This is all defined by established technical standards, such as Ethereum's ERC-721 (a specific rulebook for creating unique tokens on the Ethereum blockchain). There are countless NFT use cases , from digital art to ticketing, but their role in verifying documents is particularly powerful.
Why It Matters: So, what makes an NFT non-fungible? Here's the best way to think of it: an NFT is a digital certificate of authenticity and ownership all rolled into one. It serves as rock-solid proof that your document is real and that it belongs to you, all thanks to its permanent, verifiable spot in the blockchain "folder."

What are digital documents?
Digital documents are essentially your familiar paper diplomas, certificates, and awards. The only difference is they exist in electronic form on a computer or network.
Let's stick with our analogy for a moment. A paper diploma you can hold in your hands is a physical document. But what happens if you take a picture of it, scan it, or create a PDF version? That file is now a digital document.
However, with simple digital files, such as a PDF diploma that doesn't protect against fraud, there's a big problem: just like paper documents, they are surprisingly easy to forge with editing software. This brings up a critical question: are digital documents secure? In many cases, the answer is unfortunately no. And this isn't just a small issue; document fraud is a massive global problem, with the latest statistics revealing shocking figures. This is where the importance of digital documents security becomes crystal clear. Some startling facts were revealed in a study by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE) . It turns out that organizations annually lose around 5% of their revenue to fraud, and document forgery is a major contributor to that loss.
You might have already seen secure digital documents in government apps. In those particular cases, the government itself acts as the verifier, and it does this through its secure, centralized systems. Blockchain and NFTs, however, offer a different path-a decentralized and globally accepted way to achieve that same level of trust.

What is a TTP (Trusted Third Party)?
A TTP is an independent, authoritative expert who confirms that a document is real and also confirms it belongs to the person presenting it.
Imagine you have landed a dream job interview with a company in another country. To verify your qualifications, they need to see your diploma. Sending the original is risky, but even if you send a copy, how can they be sure it's the real deal?
This is exactly the kind of problem a TTP (Trusted Third Party) is designed to solve. So here is the concept of a Trusted Third Party (TTP) explained .
Here’s what a TTP does:
- It checks with your university to confirm the diploma is legitimate.
- It verifies that the diploma was, in fact, issued to you.
- It then acts as a trusted middleman, passing the verified information to the employer on its own authority.
Thanks to the TTP, the employer gets reliable information from a source they can trust, and you get to prove your credentials without any hassle. Why do you need a Trusted Third Party (TTP)? Because in the traditional world, it's one of the only ways to establish trust between two parties who don't know each other. What’s particularly interesting is this: blockchain systems are often called "trustless" precisely because their security, which is based on code, aims to make a human TTP entirely unnecessary.

What is a CA (Certification Authority)?
A CA is an organization that checks and confirms an important detail: it confirms that the creator of the documents, like a university, has the right to issue them.
So, the TTP helped the employer trust that your diploma is authentic. But this raises another important question: how do we know the university that issued it isn't just a "diploma mill" (a fraudulent company that sells fake academic degrees)?
This is where a CA (Certification Authority) comes into play. So, what is a Certification Authority (CA)? The job of a CA is to verify the source of the document itself. It confirms that the university is a legitimate, accredited (officially recognized) institution and also ensures that it has the legal authority to issue diplomas. This adds another critical layer of security. This process makes sure not only that your document is authentic, but it also proves the institution behind it is real and reputable.
What is the role of a Certification Authority (CA)? It works much like the system that secures websites. When you see a padlock icon in your browser, a CA is at work. The CA has verified that the website is legitimate and not an imposter, all thanks to a digital certificate like an SSL/TLS certificate.

What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is a set of rules you must follow to interact with the blockchain. In it, all possible actions and their consequences are clearly defined.
Let's go back to our blockchain folder. What is a smart contract? Imagine your NFT diploma is inside, securely glued into the chain. You can't just walk in and handle it yourself. The folder is kept in a secure room with an administrator at the door. To do anything, you have to tell the administrator what you need. He then pulls out a rulebook, finds the procedure for your request, and follows the instructions exactly.
In this scenario, that rulebook is the smart contract. The crucial difference here is that in the world of blockchain, the "administrator" is actually computer code that runs automatically, without any human involvement. What's more, its rules can't be changed once it's launched. This idea isn't new; the computer scientist Nick Szabo first described the concept way back in 1996 . As he explained it, smart contracts are designed to "formalize and secure relationships over computer networks," essentially making agreements binding through code. ( You can read more about the foundational concepts here ). How do smart contracts automate agreements? This automation eliminates both human error and bias. For example, a rule within a smart contract might be to "issue a diploma once payment is made and courses are completed." The very moment those conditions are met, it will execute that command instantly and flawlessly. Today, platforms like Ethereum have made smart contracts a foundational building block of the decentralized web.
What is a cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is the "currency" of a specific blockchain. Just as a national currency is tied to a country, a digital currency is tied to a particular blockchain.
So, what is cryptocurrency and where does it fit into all this? That automated administrator (the smart contract) doesn't work for free. To execute its code and perform tasks on the blockchain, it needs to be paid. But it doesn't accept dollars or euros. Instead, it only accepts special tokens that are native to its own blockchain system.
These tokens are the cryptocurrency. What is the purpose of cryptocurrency on a blockchain? It's not just for speculation; it's the fuel that powers the network's operations. To perform an action on the blockchain, such as issuing a new NFT diploma, you first need to have some of this currency. You then use it to pay the "administrator" for its work. These transaction fees are often called gas fees -a key factor in the cost of issuing digital credentials-and they are used to reward the network participants who lend their computing power, which keeps the entire system running securely and efficiently. This begs the question, can blockchain be used for more than just cryptocurrency? The answer is a resounding yes, as we've seen with NFTs and smart contracts.

Want to dive deeper into the technical details?
You’ve just mastered the core concepts with some simple, everyday analogies. Are you ready to solidify that understanding? Here's a quick-reference glossary with more formal definitions. It's a great way to reinforce what you've learned, and you'll get clear, to-the-point explanations.
A Quick Technical Glossary
- Database: This is a structured system designed for storing and retrieving digital data. It is typically centralized , meaning a single entity controls it, and it is also mutable , which allows data to be easily created, read, updated, and deleted (CRUD). Understanding this is key to the blockchain vs database discussion.
-
Blockchain (Centralized/Private):
Answering
what is blockchain
in a corporate setting often leads here. This is an immutable (unchangeable) digital ledger controlled by a single organization. It uses the same core technology of linked blocks to ensure data integrity; however, all control over the network is
centralized
.
- Centralized Control: The owner decides who can view the ledger, who can submit transactions, and who can validate new blocks.
- Immutable: Just like its public cousin, records can't be changed once they are added. This creates a tamper-proof audit trail, making this model great for enterprises that want security without giving up control.
-
Blockchain (Decentralized, Public):
This is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable digital ledger.
- Decentralized/Distributed: The ledger is copied and then spread across many different computers, a structure that removes the need for a central authority.
- Immutable: Its records are contained in cryptographically linked blocks. Once a block is added, its data cannot be altered, as changing it would require altering all of the blocks that come after it.
- NFT (Non-Fungible Token): If you're asking what is an NFT , this is the technical answer. It is a unique cryptographic token on a blockchain that represents ownership of a specific asset. Its uniqueness comes from its distinct metadata as well as a unique token ID. The term "Non-fungible" means that it is one-of-a-kind and therefore cannot be replaced one-for-one with another token.
- Digital Documents: In this context, this refers to any document that exists in a digital format. The key difference is that a simple file, like a PDF, is easily copied and forged. In contrast, a cryptographically secured document , such as an NFT, is different because its authenticity and ownership can be proven on a blockchain.
- TTP (Trusted Third Party): This is the TTP explained : an external group that helps to secure interactions between various parties. A TTP provides trust by verifying identities or validating transactions, and they can also act as an escrow agent (a neutral party that holds assets until certain conditions are met).
- CA (Certification Authority): So what is a CA? It is a specific kind of TTP that issues digital certificates. These certificates are then used to verify that a public key (a long, cryptographic code) belongs to a specific person or company. This verification process ensures the authenticity of the certificate holder.
- Smart Contract: So, what is a smart contract? It's a self-executing program that is stored on a blockchain and automatically runs when its pre-written conditions are met. Because it is on a blockchain, its execution is both transparent and irreversible, a feature that removes the need for a traditional middleman.
- Cryptocurrency: In short, what is cryptocurrency? It is a digital currency that uses cryptography for its security. It operates without a central bank, a feature called decentralization, and is typically based on blockchain technology. It serves as a way to exchange value and is also used to pay for transaction fees, commonly known as " gas ."
Want a more comprehensive exploration? Our full guide is waiting for you. It covers everything from history to advanced implementation. Check it out: NFT Credentials, Diplomas, Certificates in Education: The Complete Guide to Digital Documents .
In it, you will find detailed information for advanced study, presented in understandable language.

Summary: From Simple Folders to a Revolution in Digital Trust
So, where has our journey through these new technologies brought us? At its heart, this system is all about building trust, especially in a digital world where faking things is often incredibly easy.
We started with a simple analogy to make sense of it all. We talked about the difference between a traditional database and a blockchain . Think of a database as a flexible ring binder. Its pages can be secretly changed. A blockchain , on the other hand, is like a special folder. Each new page is permanently and irreversibly glued to the last. This one core difference is immutability , or the quality of being unchangeable. It's the foundation for everything else.
This process creates a transparent and unchangeable audit trail . That's just a fancy term for a sequential record of all activities. It doesn't matter if the technology is centralized and managed by one group or decentralized and spread across a global network. Blockchain solves the fundamental problem of keeping digital documents secure.
Once you understand that secure foundation, you can see how the other pieces fit together so perfectly. An NFT (Non-Fungible Token) is just one of the "pages" glued into our blockchain folder. It serves as your unique, verifiable digital document.
To manage how these important documents are handled, we use smart contracts . You can think of these as automated rulebooks. They execute actions without needing a human middleman. This ensures fairness and eliminates errors. Of course, an automated system like this needs fuel to run. That's precisely the role of cryptocurrency . These are the native tokens used to pay for any transactions on the network.
This powerful, self-governing ecosystem, which offers tangible benefits for universities, students, and employers, is a world away from traditional methods. In the old world, we have to rely on a TTP (Trusted Third Party) to act as a human verifier. We also need a CA (Certification Authority) . They confirm that the organization issuing a document is legitimate. While these processes work, let's be honest: they can be slow, contribute to the hidden costs of verification, and are highly centralized.
The dynamic combination of blockchain, NFTs, and smart contracts offers a new path forward. It's a "trustless" system. Here, security isn't guaranteed by a person or a single company. Instead, it's guaranteed by transparent, unchangeable code. This technology is paving the way for the future of digital academic credentials. It’s a future where your digital achievements can be verified instantly and securely, from anywhere in the world.
➡️ What's the next step? You know what the technologies are. The next question is why they are so critical for this application. Understand why blockchain and NFTs are absolutely essential for credential verification.

The Future of Digital Credentials (Powered by eGAB)
How to Issue and Manage NFT Credentials on eGAB: A Non-Technical Guide
What Does an NFT Diploma Look Like? A Real-World Example on eGAB
What Is the Cost of Issuing Digital NFT Credentials on the Global Academic Blockchain?
The ROI of NFT Credentials: How to Calculate Payback for Universities
